What is Agile Testing?

Key Principles of Agile Testing
1. Continuous Testing
-
Testing happens at every step of the development process.
-
Bugs and errors are found and fixed early, preventing bigger problems later.
2. Test-Driven Development (TDD)
-
Test cases are written before any code is developed.
-
The code is then created to pass these tests, ensuring functionality from the start.
3. Collaboration
-
Developers, testers, and stakeholders work together closely.
-
This teamwork helps everyone stay aligned with project goals.
4. Customer Focus
-
Agile Testing ensures that the software meets the actual needs of the end-users.
-
The focus is on delivering value to customers.
5. Flexibility
-
Agile Testing easily adapts to changing requirements.
-
It is perfect for projects where needs can evolve quickly.
6. Automation
-
Automated testing tools are used to save time and improve accuracy.
-
This is especially useful when testing needs to be repeated often.
Agile Testing Methodologies
1. Test-Driven Development (TDD)
-
Write test cases first, then develop code to meet these tests.
-
This ensures clean and functional code from the beginning.
2. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD)
-
Focuses on how the software should behave.
-
Uses simple, everyday language to define features and tests.
3. Acceptance Test-Driven Development (ATDD)
-
Involves stakeholders in defining acceptance tests before coding begins.
-
Ensures the final product aligns with business needs.
4. Exploratory Testing
-
Testers explore the software in creative ways to uncover unexpected issues.
-
This is not pre-planned and relies on the tester’s expertise.
5. Continuous Integration and Testing
-
Code changes are integrated regularly, and automated tests are run frequently.
-
Provides quick feedback and ensures stability.
Agile Testing Strategies
1. Iterative Development
-
Each development cycle (iteration) includes testing.
-
This ensures rapid feedback and constant improvement.
2. Whole Team Responsibility
- Everyone on the team, including developers, testers, and stakeholders, is responsible for the quality of the product.
3. Continuous Feedback
- Regular feedback from users and clients helps improve the product throughout development.
4. Automated Regression Testing
- Automating repetitive tests ensures the software remains stable as changes are made.
Agile Testing Parts: Understanding the Four Key Areas

Part 1: Technical Tests to Support Development
-
Unit Testing: This checks individual pieces of code (called units) to make sure they work correctly. For example, a single function or method in your software is tested in isolation.
-
Component Testing: This looks at larger pieces of the software, like a group of related functions or a specific feature, to confirm they work together as expected.
Part 2: Business-Facing Tests for Validation
-
Functional Testing: Checks whether the software works as expected based on the requirements. For instance, if a login feature is supposed to let users access their accounts, functional testing ensures it does just that.
-
User Experience Testing: Focuses on how users interact with the software. This includes checking if it’s easy to navigate, understand, and use.
Part 3: Exploratory and Usability Tests for User Perspective
-
Exploratory Testing: Testers actively explore the software without predefined scripts. This helps uncover unexpected bugs or issues that scripted tests might miss.
-
Usability Testing: This examines how user-friendly the software is. For example, does the design make sense? Can users complete tasks quickly and easily?
Part 4: Technical Tests for Performance, Security, and Scalability
-
Performance Testing: Ensures the software runs smoothly, even under heavy use. For example, can it handle thousands of users at the same time without slowing down?
-
Security Testing: Checks for vulnerabilities that hackers might exploit, ensuring data and systems are safe.
- Scalability Testing: Determines if the software can grow as needed, like handling more users or larger amounts of data.
The Agile Testing Life Cycle: A Step-by-Step Process
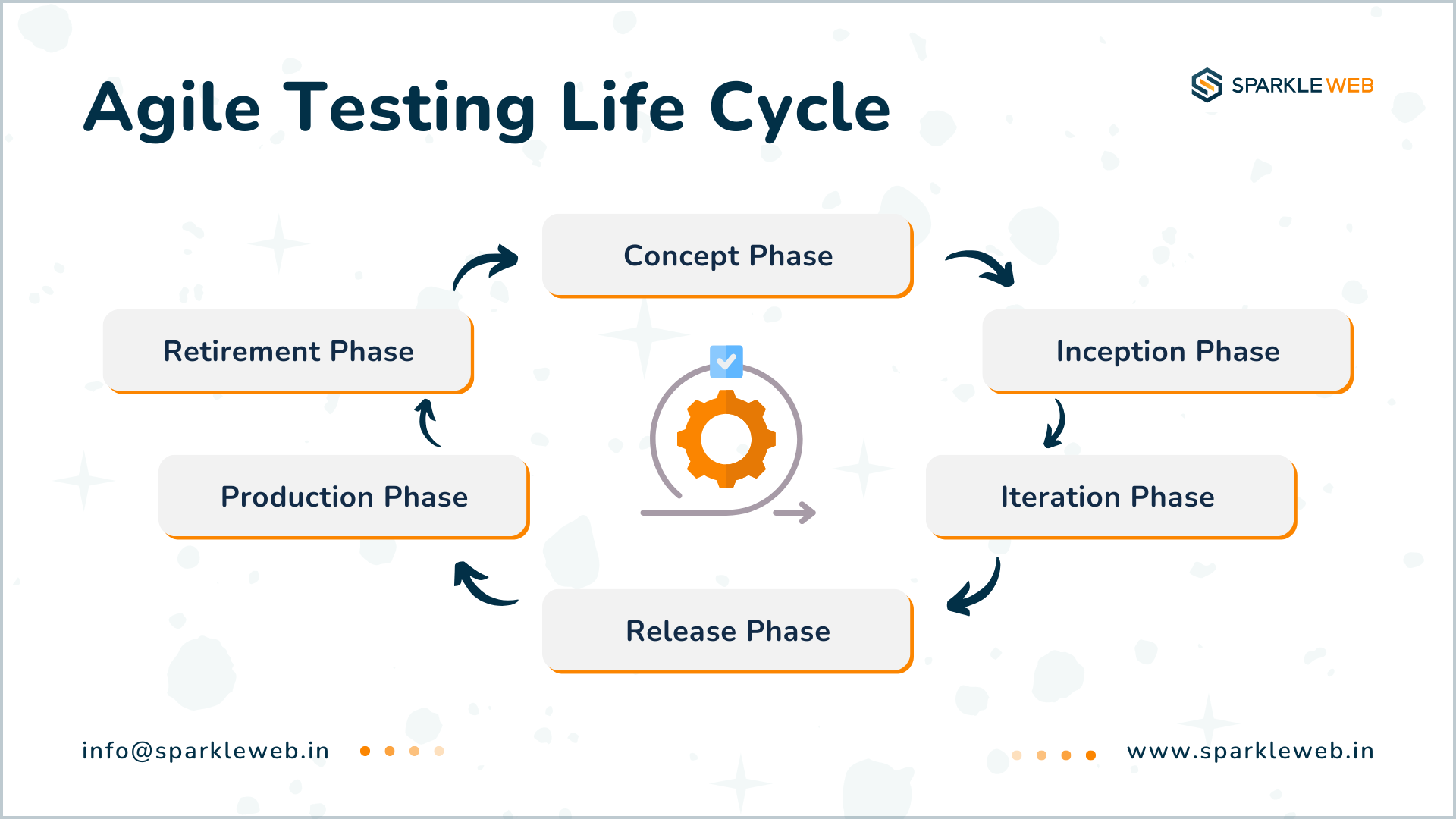
1. Concept Phase: Setting the Foundation
-
Identify the scope of the project: What features will it have? Who will use it?
-
Define objectives: What problems will the software solve?
- Plan the testing strategy: Decide how testing will be done and what tools to use.
2. Inception Phase: Laying the Groundwork
-
Set up testing environments: Create spaces where the software can be tested safely without affecting real users.
-
Create initial test strategies: Decide what tests to perform first and how to prioritize them.
3. Iteration Phase: Testing Alongside Development
-
Write and execute test cases: Testers create specific scenarios to check how the software behaves.
-
Perform regression testing: Ensure new changes don’t break anything that was already working.
- Collaborate closely with developers: Testers and developers work together to fix issues quickly.
4. Release Phase: Final Testing Before Deployment
-
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): End-users test the software to confirm it meets their needs.
-
Beta Testing: A small group of users tries the software in real-world conditions, helping identify any last-minute issues.
5. Production Phase: Monitoring and Feedback
-
Monitor performance: Keep an eye on how the software is working in real-world use.
-
Address feedback: Fix any issues users report and make improvements based on their suggestions.
6. Retirement Phase: Closing the Project
-
Archive data: Save important information for future reference.
-
Migrate systems: Move users and data to new software if necessary.
Benefits of Agile Testing
1. Early Bug Detection
-
Bugs are identified and fixed early in the development process.
-
This saves time, money, and effort compared to fixing issues later.
2. Faster Delivery
- Continuous testing allows quicker releases without sacrificing quality.
3. Better Collaboration
- Team members work together, improving communication and understanding.
4. Higher Quality Software
- Testing throughout development ensures the final product is reliable and functional.
5. Customer Satisfaction
- Software that meets user needs and works as expected leads to happier customers.
6. Flexibility
- Agile Testing makes it easy to adapt to changes in project requirements.
Best Practices for Agile Testing: Making It Work
1. Work as a Team
-
Testing isn’t just the testers’ job. Developers, stakeholders, and testers all need to collaborate.
-
Regular communication ensures everyone knows the goals and works towards them together.
2. Prioritize Automation
-
Automate repetitive tasks like regression testing to save time and reduce errors.
-
Use tools like Selenium or JUnit to speed up testing and increase accuracy.
3. Integrate Testing Throughout Development
-
Test early and often. Don’t wait until the end of the project.
-
Continuous testing ensures that issues are found and fixed right away.
4. Focus on Coverage
-
Make sure all important areas are tested: functionality, security, performance, and user experience.
-
Use test coverage tools to track which parts of the software have been tested.
5. Improve Continuously
-
Hold regular team meetings to review what worked well and what didn’t.
-
Use feedback to refine testing processes and tools.
6. Use Metrics to Measure Success
-
Track key metrics like defect density (number of bugs per unit of code) and test coverage.
-
Use these numbers to assess software quality and improve over time.
Why Choose Agile Testing with Us?
1. Tailored Agile Testing Strategies
- We create testing strategies that fit your unique development workflows.
2. Automation Expertise
- Our team uses advanced tools to automate tests, saving you time and ensuring accuracy.
3. Collaboration-Focused Approach
- We work closely with your team to seamlessly integrate Agile Testing into your projects.
4. Scalable Solutions
- Our services grow with your business, whether you are a startup or an established enterprise.
Conclusion
Contact Us today and let’s get started!



Keyur Kinkhabwala
QA Manager
Reply