Over the last two decades, software applications have changed the way people live, work, and do business. Earlier, most software was installed directly on computers. Today, applications run across websites, mobile phones, tablets, and cloud platforms.
For example, Microsoft Office was once installed on desktops, but is now widely used via Office 365 in web browsers. Similarly, Amazon started as a website, but today millions of users shop through its mobile app.
Because applications now run on different platforms, testing them has also become more complex.
Web applications and mobile applications behave differently. They are used across different environments, devices, and user groups with varying expectations. That is why mobile app testing and web app testing are not the same.
In this article, we will explain:
- Types of testing for both platforms
All explanations are kept simple and easy to understand.
What Are Web Applications?
Web applications, often called web apps, are software programs that run on web servers and are accessed using a web browser. You do not need to install them on your device. You simply open a browser like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Edge and use them through the internet.
Web applications are usually built using technologies such as:
-
HTML (structure)
-
CSS (design)
- JavaScript (logic and interaction)
Some web apps are very simple, while others are large and complex.
Key Characteristics of Web Applications
- Updates happen on the server, not on user devices
Examples of popular web applications include Google Docs, Facebook, Gmail, and Amazon.
Types of Web Applications
Web applications can be grouped into different types based on how they behave and how users interact with them.
1. Static Web Applications
Static web applications show fixed content. The information does not change based on user actions.
They are usually built using HTML and CSS.
Examples:
These apps are simple, fast, and easy to test because the content rarely changes.
2. Dynamic Web Applications
Dynamic web applications change content based on user input or real-time data.
They usually use a backend server and database.
Examples:
These applications require deeper testing because data changes frequently, and user actions affect the output.
3. Single-Page Applications (SPAs)
Single-page applications load only one web page. When users interact with the app, content updates without refreshing the entire page.
SPAs provide a smooth and fast experience.
Examples:
Testing SPAs requires checking performance, state changes, and smooth navigation.
4. Multi-Page Web Applications
In multi-page web apps, a new page loads every time the user navigates.
They are often used for large platforms with many sections.
Examples:
Testing focuses on page navigation, loading speed, and consistency across pages.
Types of Web Application Testing
Web applications need different types of testing to ensure quality and reliability.
Functionality Testing
This testing checks whether the application works as expected.
It verifies:
Example:
Testing if a login form accepts correct details and shows an error for wrong inputs.
Interface Testing
Interface testing checks how different parts of the system communicate with each other.
It focuses on:
-
API communication
-
Data transfer
- Integration between UI and backend
It does not test individual features but ensures systems work together smoothly.
Tools Used for Web Application Testing
Some common tools include:
- JMeter – Load and performance testing
Using the right tools helps detect bugs early and improve app quality.
What Are Mobile Applications?
Mobile applications, or mobile apps, are software programs designed to run on smartphones and tablets.
They are installed directly on devices and downloaded from app stores like:
Mobile apps often use device features like the camera, GPS, sensors, and notifications.
Examples include WhatsApp, Instagram, Uber, and Netflix.
Types of Mobile Applications
1. Mobile Web Applications
These are websites optimized for mobile devices.
They:
Examples:
Mobile news websites like BBC or CNN.
2. Native Mobile Applications
Native apps are built specifically for one platform.
-
iOS apps: Swift, Objective-C
-
Android apps: Java, Kotlin
They offer high performance and full access to device features.
Examples:
WhatsApp, Instagram, Snapchat.
3. Hybrid Applications
Hybrid apps combine web and native features.
They:
Examples:
Uber, Twitter, Instagram.
Types of Mobile Application Testing
Mobile apps need extra testing because of the variety and real-world conditions.
Usability Testing
Checks if the app is easy to use.
Focus areas:
-
Button size
-
Readable text
- Simple navigation
Performance Testing
Checks how the app behaves under different conditions:
-
Low battery
-
Weak network
- High user load
Security Testing
Ensures data protection and secure access.
Checks:
-
Authentication
-
Authorization
- Data storage security
Interruption Testing
Tests the app's behavior during interruptions like:
-
Incoming calls
-
SMS
- Low battery alerts
Compatibility Testing
Ensures the app works on:
-
Different devices
-
Different screen sizes
- Different OS versions
Localization Testing
Checks language, currency, date format, and region-specific settings.
Installation Testing
Verifies:
Tools Used for Mobile App Testing
Popular tools include:
- Detox – End-to-end testing
-
JMeter & LoadRunner – Performance testing
-
OWASP ZAP & Kiuwan – Security testing
-
Testlio – Crowd testing on real devices
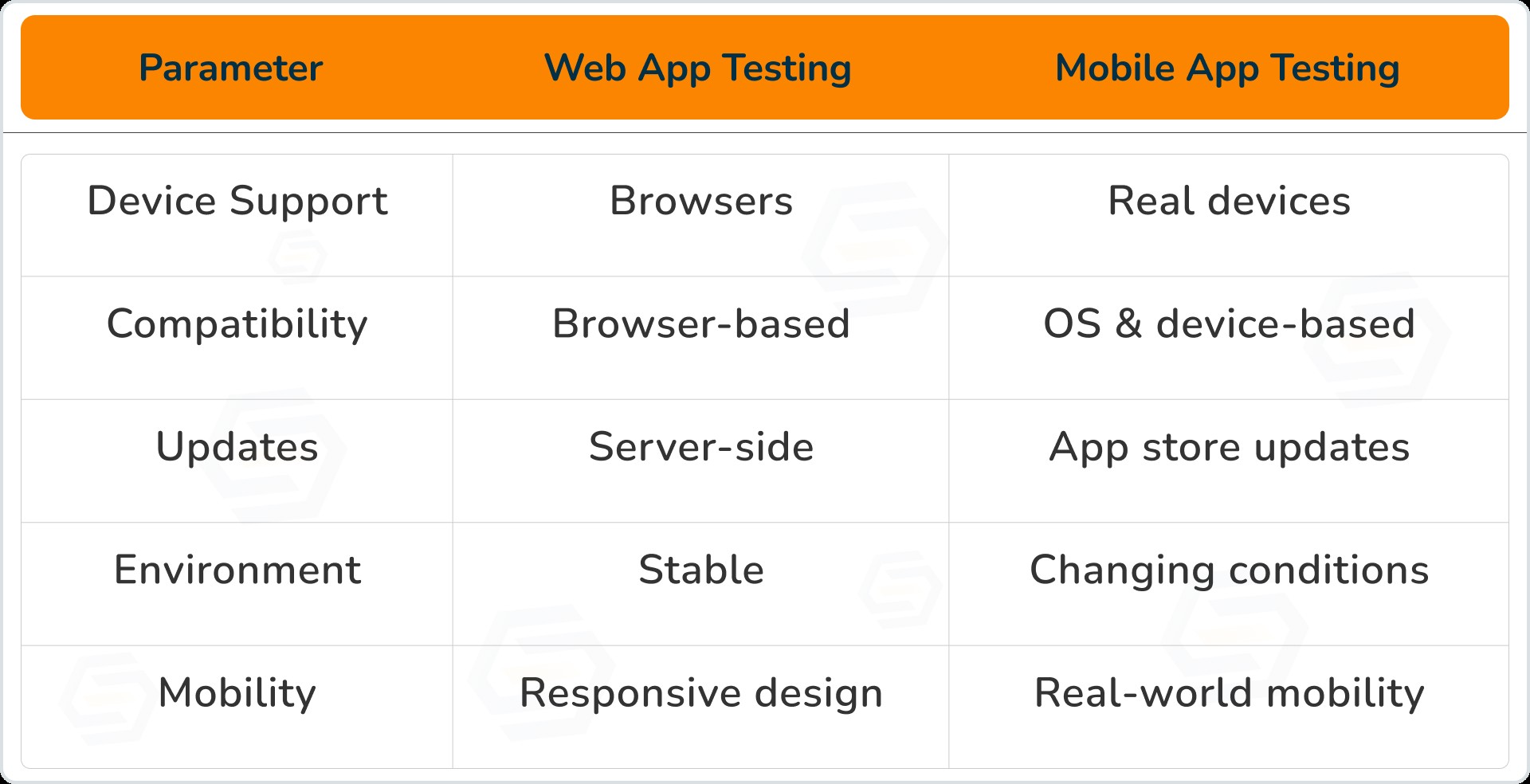
Difference Between Web App Testing and Mobile App Testing
Importance of Real Devices and Crowd Testing
Testing on real devices gives accurate results.
Benefits:
Crowd testing platforms provide access to many devices without extra cost.
Final Thoughts
Web and mobile applications may look similar, but testing them requires different strategies.
Understanding these differences helps businesses:
-
Reduce bugs
-
Improve user experience
- Launch reliable products
Ready to Deliver Bug-Free Software?
Partner with
Sparkle Web to build, test, and scale high-quality web and mobile applications.
Contact us today and test your strength, not your weakness.


Sumit Patil
A highly skilled Quality Analyst Developer. Committed to delivering efficient, high-quality solutions by simplifying complex projects with technical expertise and innovative thinking.
Reply