What is Payment Testing?
-
When a user clicks “Pay”
-
When the money goes through a payment gateway
- When it reaches the company account
- When confirmation emails or receipts are sent
-
Users can pay without facing errors.
-
Payments are safe and encrypted.
- The app follows industry rules like PCI DSS.
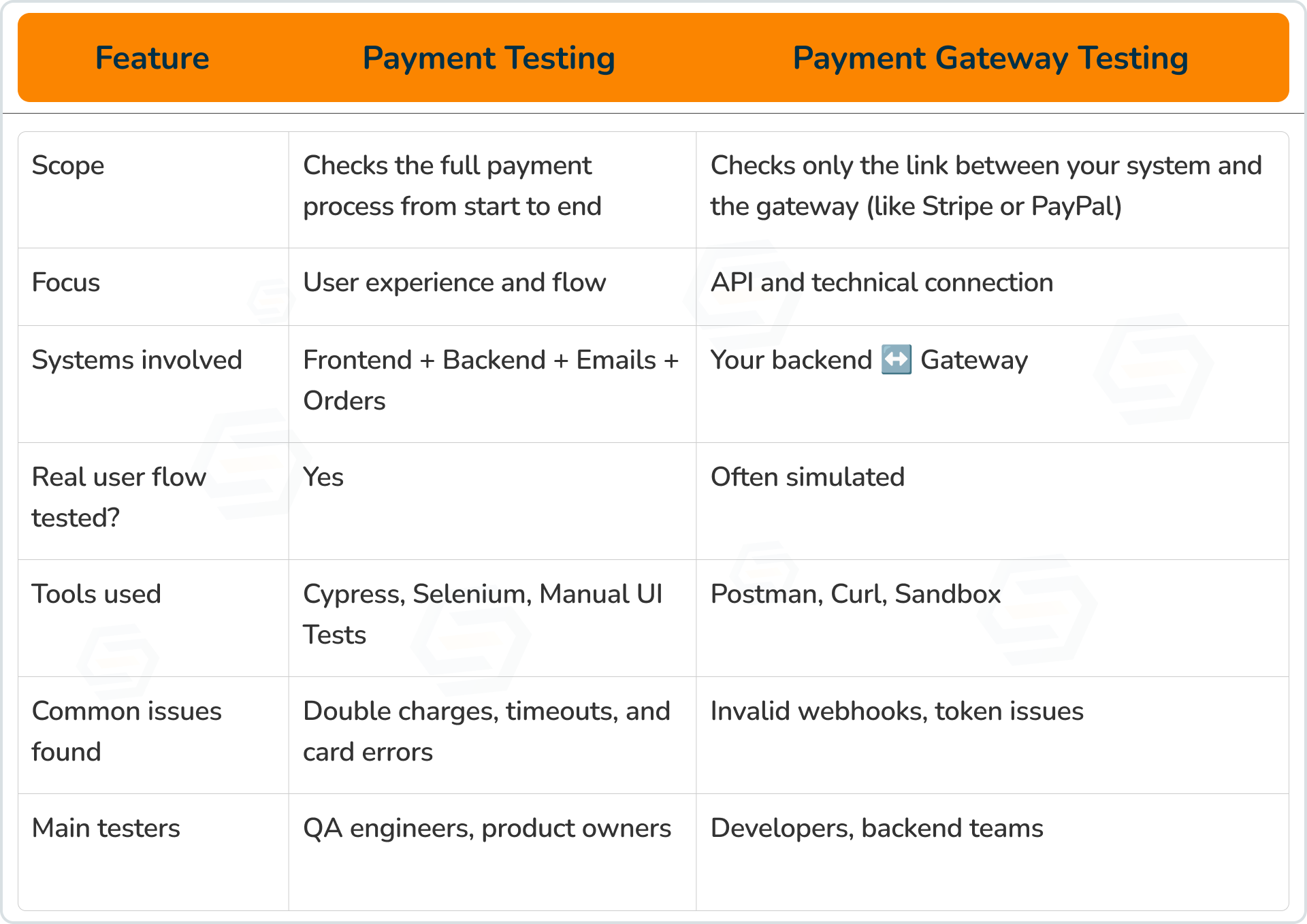
Payment Testing vs Payment Gateway Testing
-
Payment testing looks at how the user pays and what they experience.
-
Payment gateway testing looks at how your app and the gateway “talk” to each other.
Real-World Examples
Payment Testing Examples
-
A customer buys a product, adds a discount code, enters the correct card details, and receives a payment confirmation message and email.
-
A customer enters an expired card and gets an error “Card expired.”
- Double-clicking the “Pay” button doesn’t charge twice.
- If the customer cancels midway, the cart restores properly.
Payment Gateway Testing Examples
-
Simulate a failed payment by using an invalid API token in Stripe’s sandbox.
-
Check how your backend reacts when PayPal sends a “Payment Failed” message.
- Test if 3D Secure (OTP or verification page) returns correctly to your site.
- Simulate delays and confirm that your app marks payments as “pending” instead of “failed.”
When and Why to Use Each Testing Type
-
Validate the full checkout process.
-
Test unusual cases (expired cards, low funds, retries).
- Ensure the user gets a smooth experience across devices.
-
Check secure data exchange via APIs and webhooks.
-
Add or change a payment provider (like Razorpay or PayPal).
- Test advanced features (3D Secure, subscriptions, saved cards).
Types of Payment Testing
1. Functional Testing
2. Usability Testing
3. Security Testing
4. Integration Testing
5. Performance Testing
6. Load Testing
7. UI Testing
8. Localization Testing
Payment Testing on Real Devices
-
Cards work in different regions.
-
Taxes, currencies, and addresses display correctly.
- Mobile wallets like Apple Pay or Google Pay function as expected.
-
Online Payments: Bank transfers, e-checks, and wire transfers.
-
Mobile Apps: PayPal, PhonePe, Venmo.
- Buy Now, Pay Later: EMI or point-of-sale credit.
- Contactless: NFC cards, digital wallets, and wearables.
-
Digital Wallets: Apple Pay, Google Pay.
-
Cryptocurrency: Bitcoin, Litecoin, etc.
How to Test Payment Functionality
Common Payment Testing Use Cases
1. Credit Card Validation
2. Connection Status
3. Payment Confirmation
4. Verify Transaction Data
Practical Testing Scenarios
Successful Transaction
-
Is the transaction logged correctly?
-
Does the user get confirmation and an email?
- Are discounts and taxes applied correctly?
Failed Payment
Timeout or Delay
3D Secure (OTP/Verification)
Load Testing
Refunds and Reversals
-
Correct amount refunded.
-
Status updates in both the app and the gateway.
- User receives refund notification.
Mobile Testing
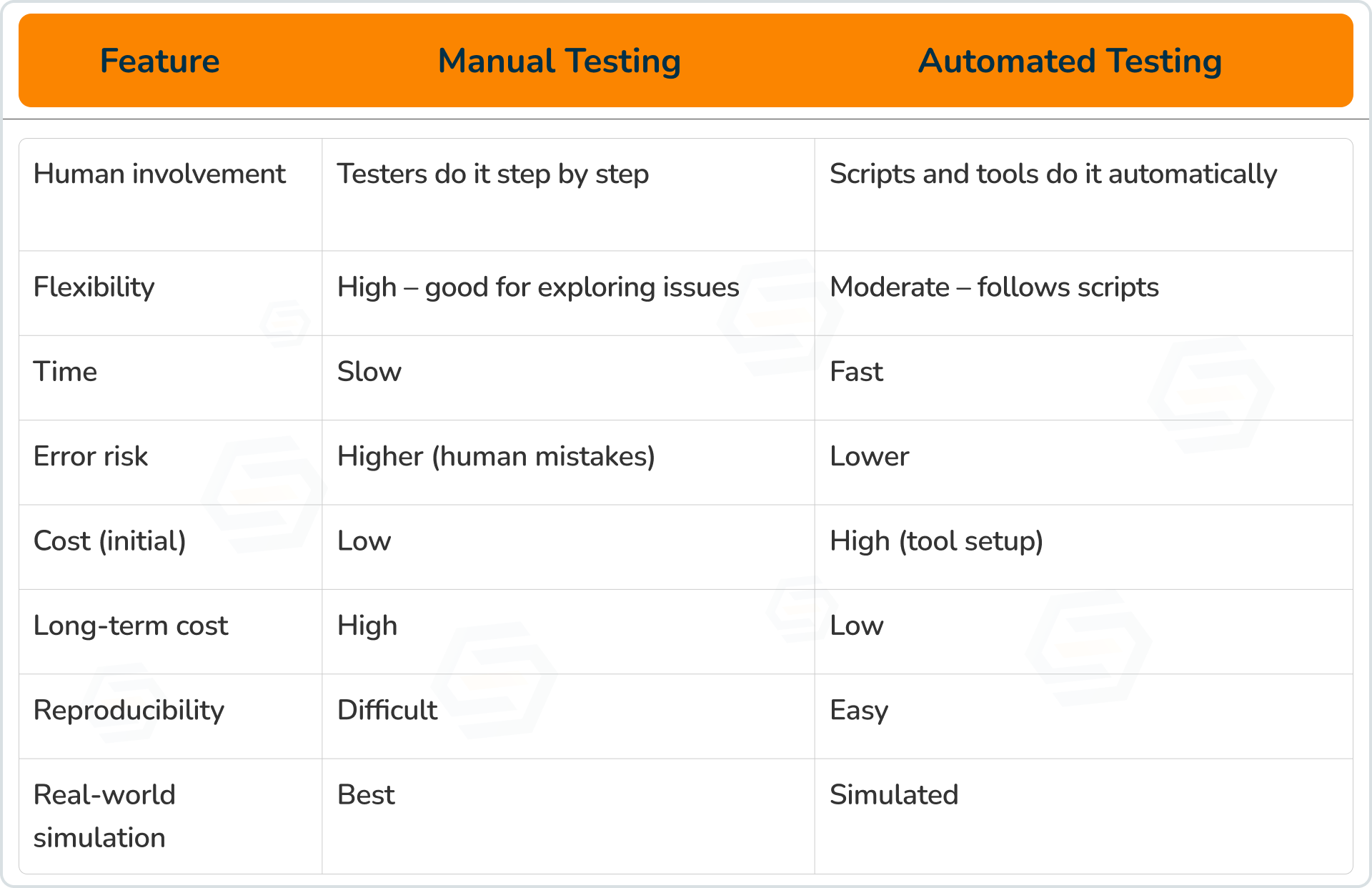
Manual vs Automated Payment Testing
-
Manual testing is better for checking user experience and real card behavior.
-
Automation is great for testing repetitive flows quickly and consistently.
End-to-End (E2E) Coverage
-
Network variations (slow/fast connections)
-
Device differences (mobile/desktop)
- Multiple payment types
- Handling failed transactions
Conclusion: Why Payment Testing Matters in 2025
-
Works perfectly across all devices and currencies
-
Stay 100% compliant with gateways like Stripe, PayPal, and Razorpay
- They are tested on real devices for real-world accuracy
- Handle high traffic smoothly with load testing
-
Use automation for faster, error-free releases



Sumit Patil
A highly skilled Quality Analyst Developer. Committed to delivering efficient, high-quality solutions by simplifying complex projects with technical expertise and innovative thinking.
Reply