-
What beta testing is
-
Why is it important
- Its benefits
- Types of beta releases and testing methods
-
The steps involved in conducting a beta test
-
Its role in reducing product failure
What is Beta Testing?
-
How easy the product is to use (usability)
-
How reliable and stable it is (reliability)
- Whether all features work correctly (functionality)
- Whether it works smoothly across devices, operating systems, browsers, or platforms
What is the Purpose of Beta Testing?
-
Collect valuable user feedback for improvement
-
Understand how the product performs in different environments
- Find bugs or issues that internal teams may have missed
- Measure user satisfaction and acceptance
-
If many users struggle with navigation, developers know the UI needs improvement.
-
If users report compatibility issues on certain devices, fixes can be made before launch.
- If feedback is positive, it confirms that the product is ready.
Benefits of Beta Testing
1. Improves Product Quality
2. Uncovers Missed Bugs
3. Real User Insights
4. Informed Business Decisions
5. Customer Involvement
6. Reduces Failure Risk
7. Better Customer Satisfaction
Types of Beta Version Releases
1. Open Beta (Public Beta)
-
Available to all users.
-
Anyone can download or sign up and provide feedback.
- Helps gather a large amount of data quickly.
- Useful for stress testing, performance testing, and general usability feedback.
2. Closed Beta (Private Beta)
-
Available to a limited number of selected users.
-
Testers are usually invited by the company.
- Can include existing customers, early adopters, or paid testers.
- Provides focused and more controlled feedback.
Types of Beta Testing
1. Public Beta Testing
2. Technical Beta Testing
3. Focused Beta Testing
4. Post-Release Beta Testing
How to Create a Beta Test Strategy?
-
Business Goals: Why are you running the beta test? (e.g., to validate UI, performance, or scalability)
-
Timeline: How long will the test run (usually 4–6 weeks)?
- Beta Plan: Detailed steps of how testers will use the product.
- Approach: Instructions for testers on how to give feedback.
-
Tools: Platforms for bug tracking and feedback collection (like TestFlight, Google Play Console, or Crashlytics).
-
Rewards: Incentives for testers such as gift cards, discounts, or coupons.
-
Entry & Exit Criteria: Define when the test starts and what conditions mark its completion.
Steps Involved in Beta Testing
1. Identify Target Platforms
2. Invite Beta Testers
3. Distribute the Beta Version
4. Collect Feedback
5. Evaluate & Improve
6. Reward Testers
Use Cases of Beta Testing
-
User Experience Testing: Check if the app feels smooth and easy to use.
-
Load and Stress Testing: Test the app with many users at once.
- Device and Platform Compatibility: Ensure it works on different devices and browsers.
- Battery Usage Testing: See if the app consumes too much battery.
-
Content Testing: Validate whether text, images, and videos are engaging.
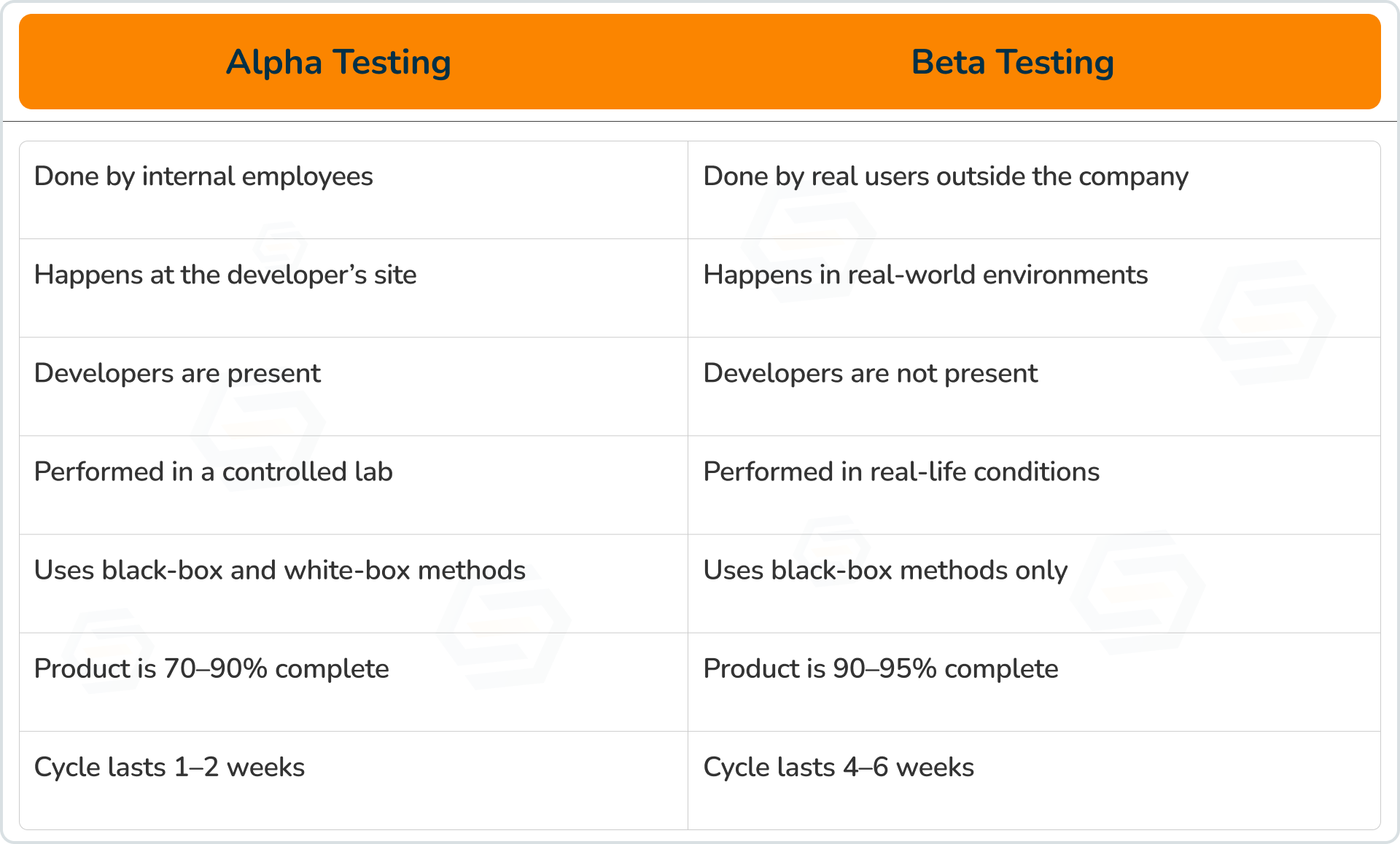
Alpha Testing vs Beta Testing
Why Beta Testing Matters
-
42% of startups fail because they release products without validating them with users.
-
Beta testing reduces product failure risk by up to 75%.
- 78% of teams that do beta testing experience higher user satisfaction.
- Apps with strong beta testing phases see 30% fewer negative reviews in their first 90 days.



Sumit Patil
A highly skilled Quality Analyst Developer. Committed to delivering efficient, high-quality solutions by simplifying complex projects with technical expertise and innovative thinking.
Reply